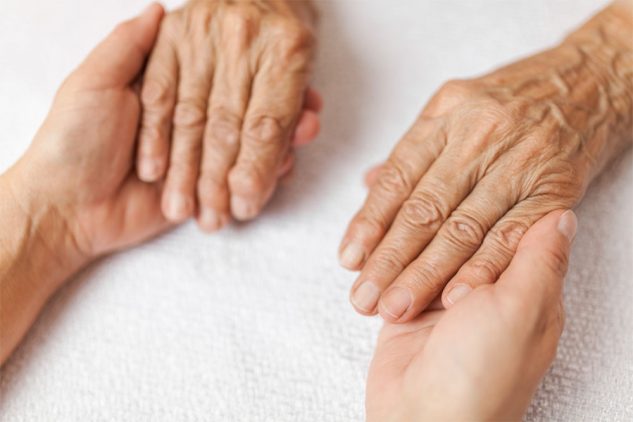
Duties of a Guardian for the Elderly
Elderly guardianship, sometimes called elderly conservatorship, is a legal relationship devised when a court names an individual to care for an elderly person that no longer can care for themselves. The named guardian has specific duties and responsibilities to the elderly individual. Read on to familiarize yourself about elderly guardianship, the process, and factors to think about below.
Why Someone Might Need a Guardian?
Regrettably, an elderly individual might become unable to care for themselves. This might include the incapacity in remembering to take necessary medications, maintain regular cleanliness, or properly handle finances. In these situations, it might be in the elderly individual’s best interests for the court to name a guardian.
What is the Guardianship Process?
Each state has their own guardianship methods and requirements. All in all, the following individuals or entities may petition the court to name a guardian:
- The elderly person themselves
- The spouse or domestic partner of the elderly individual
- A family member of the elderly individual
- A friend of the elderly individual
- A state or local government agency
The guardianship process can be long and complicated, maybe understandably, given that the elderly individual is going to lose some important rights and have their care entrusted to another individual. In California, for instance, the process takes each of the following steps:
- Filing the Petition for Appointment of Conservator form, in which requires details about the elderly individual, the one filing the petition, family members of the elderly individual, and the reasoning why guardianship is required. The petitioner needs to also clarify why options to a guardianship aren’t available or relevant.
- Notifying the elderly person, along with their family members, of the filing for petition for guardianship
- Investigation carried out by a court appointed investigator to assess whether the suggested guardianship is required.
- A court hearing in which the judge examines the petition, listens to depositions, establishes if the elderly individual lacks the capability to care for themselves, and determines whether to award the guardianship petition.
Responsibilities of a Guardian
A guardian has a responsibility of care towards the elderly individual. Simply put, this means that the guardian needs to put the elderly individual’s best interests first.
The guardian might have a lot of responsibilities, like deciding where the elderly person is going to live, how to retain the elderly individuals health, how to create a budget based on the elderly individuals finances, and how to schedule for recreational activities and social contact. To give you an idea of the many possible responsibilities that it takes, California’s handbook for named guardians is upwards of three hundred pages.
Pros and Cons of Elderly Guardianship
The objective and anticipated benefits of elderly guardianship is that an elderly individual that can longer care for themselves receives adequate care. Nevertheless, there are a multitude of disadvantages that could come with guardianship.
Guardianship petitions are typically costly. There are a lot of forms to fill out, a lot of procedural requirements, and probably many court hearings. When there is any objection to a suggested guardianship, maybe by the elderly individual or by family members, the process becomes even more convoluted and may be emotionally and financially straining.
Guardianship, by definition, requires the elderly individual to lose some of their rights. For instance, the elderly individual might lose the right to manage their finances, to choose their own caregiver, and to decide where they are going to live. There’s also the chance that the guardian is going to fail to act in the elderly individual’s best interest.
Alternatives to Guardianships
Courts regard elderly guardianship to be the last recourse because of the aforementioned drawbacks. Subject to the state you live in, potential alternatives to guardianship comprise of:
- Living Trusts – The elderly individual can name in individual to manage financial affairs. Obtain a DIY living trust at a small cost.
- Representative Payeeship – When the elderly person’s income is from governmental benefits, they may name an individual to oversee this income.
- Power of Attorney – The elderly individual may give another individual the right to act on their behalf. Obtain a DIY POA form online.
- Stand-by Guardianship – In many states, the elderly individual may name someone as a stand-by guardian, in case the individual loses the capability to care for themselves.
Note that all these alternatives involve the elderly individual willingly assigning their rights to another individual. When the elderly individual becomes unable to do so because of mental incapacitation, then these alternatives will be no longer available.
Getting Legal Assistance
Elderly guardianships are complicated and have important outcomes. When you’re thinking about guardianship for yourself or for a loved one, or when you’re contemplating about serving as a guardian, you should meet with an attorney that specializes in elder law.
Source:
-
Elderly Guardianship Basics. (2021, March 12). Retrieved April 13, 2021, from https://www.findlaw.com/elder/elder-care-law/elderly-guardianship-basics.html
Arizona Family Law
Naming guardians in your will can be part of your estate plan. You may think you’re too young or don’t have enough money to justify the expense, but if you have children, you have priceless assets. There are many considerations when naming guardians for your kids. However, the process doesn’t have to be expensive or complicated.
There’s nothing better than the peace of mind you will have knowing you’ve protected your family at a time when they need it most. Let us help. Schedule a consultation or contact Ogborne Law, PLC of Arizona today.
Engaging with an attorney to protect your family is never an easy step. Whether you need to protect your family from the unthinkable or restructure your family through collaborative divorce, we’re here to help. When you’re ready to schedule a consultation with Michelle Ogborne, please visit the scheduling page to get started.